Introduction to Basic Toilet Components
Understanding the basics parts of toilets components is crucial for both homeowners and those interested in plumbing. The toilet may appear simple, but it’s a complex fixture with many essential parts. These parts can be categorized into two main areas: the tank and the bowl. The tank is the upper part that holds water in reserve until the next flush, while the bowl is where waste is deposited and flushed away.
The toilet’s operation relies on a set of interconnected parts that function in harmony. When you press the handle, the chain lifts the flapper, releasing water from the tank into the bowl. The fill valve then refills the tank, and the overflow tube ensures the water level stays consistent. Each part of the toilet tank has a designated role, from water delivery to maintaining the correct water level.
In the bowl section, the O-ring and wax ring play vital roles in preventing leaks. The toilet floor flange anchors the toilet to the ground and connects it to the sewage system. Recognizing these parts is the first step in troubleshooting any toilet issues you might encounter.
As we explore further, we’ll dive into the detailed anatomy of the tank components, and examine the toilet bowl in depth. Understanding the fundamentals of these parts will help you tackle common toilet problems and keep your toilet running smoothly. Stay tuned for insights into common issues, installation tips, and the future of toilet design as we continue our exploration of toilet components.

Detailed Anatomy of the Toilet Tank
The toilet tank, often unnoticed, is a hive of activity. Behind its ceramic exterior lies a system that orchestrates each flush.
The Tank Setup
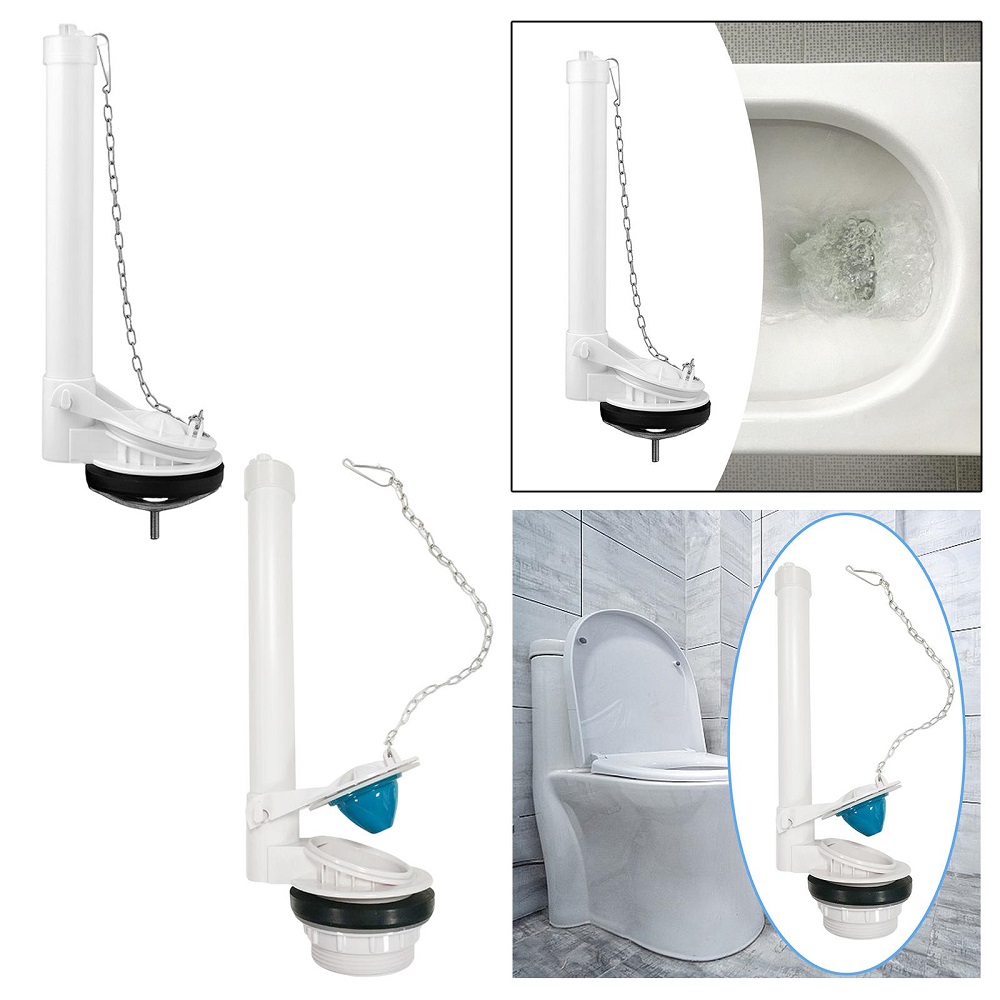
The tank’s role begins when you decide it’s time for a flush. It houses components like the handle, flapper, fill valve, and float. The tank gathers the right volume of water needed for a powerful and complete flush.
How the Toilet Handle Operates
When you press the handle, you kick-start a chain reaction. The handle lifts a chain inside, which in turn raises the flapper valve allowing water to surge into the bowl.
Function and Types of the Toilet Flapper
The flapper sits at the tank’s base. It seals the water in, only opening when the handle’s action tells it to. Flappers come in rubber or plastic varieties and can degrade over time.
Overview of the Fill Valve and Its Functions
Once the flush is through, the fill valve’s job is to top the tank up again. Its job is to manage the water level, ensuring everything is ready for the next use.
Role and Functions of the Toilet Float
The toilet float, or ballcock, used to be commonplace. It floats atop the water, governing the fill valve. Newer toilets have moved on to more modern systems.
Importance of the Overflow Tube and Water Supply Line
Safety devices in their own right, the overflow tube protects against spills, and the water supply line ensures a constant flow of fresh water.
Exploring the Toilet Bowl and Its Parts
The toilet bowl is a critical component of your bathroom’s plumbing system. It’s the part you’re most familiar with, as it holds the water and waste before a flush. The design ensures efficient removal of waste and prevents unwanted odors by utilizing a trapway. The bowl also plays a significant role in the toilet’s overall aesthetic appeal, as it’s the most visible part.
The Central Role of the Toilet Bowl
The toilet bowl takes center stage in the flushing process. When the handle is pressed, water from the tank rushes in, swirling around to clean and carry away waste. This porcelain piece is durable, designed to withstand years of use. Its smooth surface helps prevent stains and makes for easier cleaning.
Utilities of the O-Ring and Wax Ring
Leaks are a no-go for toilets, and the O-Ring, positioned between the tank and bowl, prevents them. If you spot water around the base, this ring might need replacement. The Wax Ring sits underneath the bowl, creating a watertight seal with the drainage pipe. A failed wax ring can lead to leaks on the floor when you flush.
Stability Provided by the Toilet Floor Flange
The floor flange is key to a wobble-free toilet. It anchors the toilet to the floor and connects it to the drainpipe. Proper installation of the flange keeps your fixture steady and secure. Its role is simple but essential; without it, leaks and movement could lead to significant problems.

Common Issues with Toilet Parts and Their Solutions
Even the best-designed toilets face common issues that can disrupt daily operations. Recognizing these problems and understanding their solutions can save you time and money. Below, we’ll discuss frequent toilet problems and provide effective solutions.
Continuous Running or Leaking
A toilet that won’t stop running often has a flawed flapper or fill valve. Replacing the leaking flapper or adjusting the fill valve usually fixes this issue.
Weak Flush or Partial Flushing
A weak flush might suggest clogged holes under the rim of the toilet bowl. Cleaning these rim holes can restore full flushing power.
Toilet Takes Too Long to Refill
A slow-filling toilet often points to a problem with the water supply line or fill valve. Checking and cleaning the fill valve or replacing the water supply line can solve this.
Water Leaks Between the Tank and Bowl
If there’s water leaking between the tank and bowl, it’s typically due to a worn out O-ring. Replacing the O-ring should stop the leak.
Water on the Floor Around the Toilet
Water on the floor might indicate a failed wax ring. Replacing the wax ring will usually prevent future leaks.
By addressing these common issues, you can ensure that your toilet maintains optimal performance and stays in good shape for years.
Installation Insights for Standard Toilet Components
Installing standard toilet components correctly is crucial for preventing future issues. Here are some key points to consider when working with the parts of the toilet.
Preparing for Installation
Before you begin, ensure you have all necessary tools and parts. Turn off the water supply to avoid any mess. Measure carefully to guarantee the components fit well.
Installing the Toilet Tank
Attach the tank securely to the bowl using bolts. Confirm the tank is level to prevent water leaks. Connect the handle and check the chain for proper length.
Setting the Toilet Bowl
Place the bowl over the drainage hole carefully. Use a new wax ring to guarantee a tight seal. Secure the bowl to the floor with the attaching bolts.
Attaching the O-Ring and Wax Ring
Fit the O-ring between the tank and bowl to prevent leakage. Position the wax ring around the toilet drain to create a watertight seal.
Finalizing the Water Supply Line
Link the water supply line to the tank’s base. Open the shut-off valve to check for leaks. Make sure connections are tight but do not over-tighten.
Following these steps will lead to a successful installation, and contribute to the longevity and efficiency of your toilet. Remember to double-check each component after installation to prevent any issues.
Future Innovations and Advances in Toilet Design
The evolution of the [parts of the toilet] continues as advancements in technology emerge. Innovations aim to enhance user experience, conserve water, and integrate smart technology for enhanced functionality.
Water Conservation and Efficiency
Upcoming toilet designs focus on reducing water usage. Dual-flush systems and low-flow toilets are becoming standard, with improvements aimed at providing effective flushes using less water. These systems help save millions of gallons of water annually.
Smart Toilets and Tech Integration
Smart toilets are on the rise with features such as self-cleaning functions, seat warming, and automatic flush. Tech integration allows for personalized settings, including user detection and hygienic improvements.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Eco-friendly materials are being explored for future toilets. Manufacturers are looking at sustainable options that reduce environmental impact without sacrificing durability or performance.
Compact and Space-Saving Designs
As living spaces become smaller, the demand for compact toilets grows. Future designs will focus on space efficiency without compromising comfort or efficiency.
Enhanced Hygiene and Maintenance
Advances in hygiene include antibacterial surfaces and touchless components. Maintenance is made easier with coatings that resist staining and reduce the need for harsh cleaning chemicals.
The future of toilet design holds promise for better environmental sustainability, user convenience, and hygiene standards. Innovations will continue to redefine the humble toilet, making it a central part of modern, eco-conscious homes.


