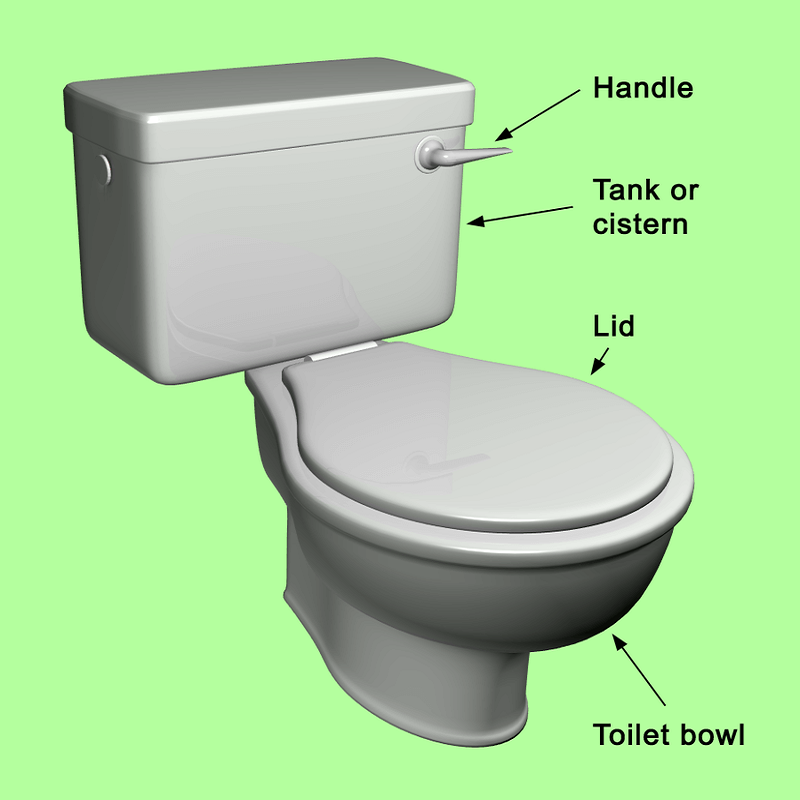
Introduction to Toilet Tank Operation
The toilet tank is a key player in your bathroom’s function. It holds the water needed for flushing away waste. It’s a behind-the-scenes hero that makes a clean and fresh bathroom possible. This section of our blog will dive into the operation of the toilet tank. We’ll explore its vital components and how they work together to keep things flowing.
The operation of the toilet tank starts when you press the flush handle. This handle is connected to the tank’s lever arm. When the lever lifts, the toilet flapper (a rubber valve) rises too. Water then gushes from the tank into the bowl, taking the waste with it. As the tank empties, the fill valve kicks in, refilling the tank and bowl with water. Finally, the flush valve ensures the process is smooth and leak-free.
Every part inside the tank has an important role. From the flush handle to the tank-to-bowl gasket, all ensure a tight seal and efficient flushing. We will walk through these elements, detailing their function and importance. By understanding your toilet tank’s anatomy, you will be better equipped to handle common issues and maintain your toilet’s performance.
In the following sections, we’ll break down each component. We’ll provide insights for troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring your toilet stays in top shape. Stay tuned as we flush out the facts and help you keep your bathroom functioning seamlessly.
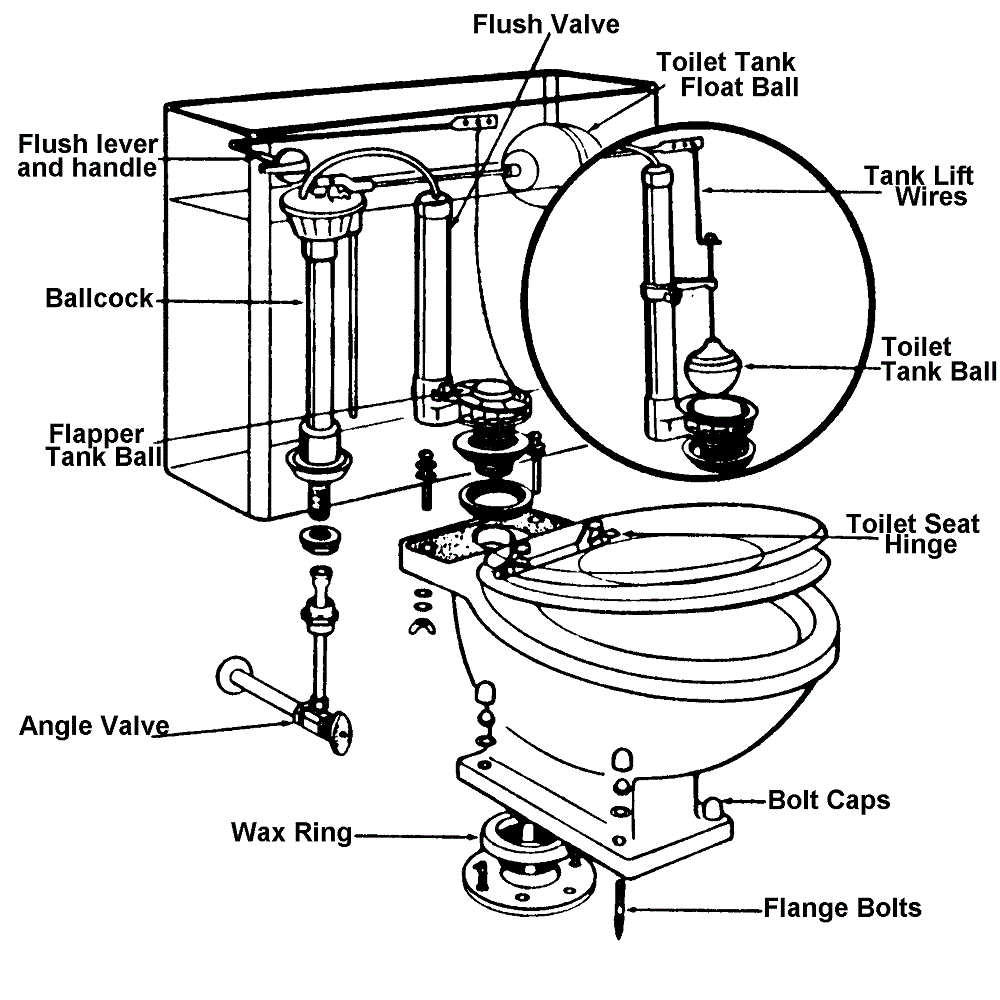
Components of the Toilet Tank
Understanding each part of the toilet tank is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting. Let’s examine the key elements that make up the inner workings of the toilet tank.
Understanding the Flush Handle
The flush handle is the first step of the flushing process. You press it down, and it moves the lever arm inside the tank. This lifts the flapper and releases water into the bowl, starting the flush.
The Role of the Toilet Flapper
The flapper is a rubber valve at the bottom of the tank. It opens to let water flow into the bowl. Then, it closes to stop the water, making sure the tank can refill for the next flush.
The Function of the Fill Valve
After flushing, the fill valve refills the tank with water. It’s a tube connected to the water supply that opens when the tank’s water level drops and closes when it’s full again.
Importance of the Flush Valve
The flush valve is the passage between the tank and bowl. It works with the flapper to release and stop water flow. This valve ensures a powerful flush and refills the tank without leakage.
Tank-to-Bowl Gasket: Securing the Seal
This gasket seals the connection between the tank and bowl. It prevents leaks, maintaining flush efficiency and saving water.
Alternate Sealing Methods: The Wax Free Seal
The Wax Free Seal is an innovative alternative to the traditional wax ring. It creates a tight, leak-proof connection between the toilet and the bathroom floor. This seal prevents water and sewer gas leaks.
Toilet Bowl and Base Essentials
The toilet bowl and base are as critical as the tank. Together, they manage waste efficiently.
Analyzing the Toilet Bowl Design
The toilet bowl design is simple but vital for the flushing mechanism. The bowl holds water and waste before flushing. Its shape aids in directing waste to the sewer. The trap underneath the bowl seals against bad odors. The anatomy of a toilet ensures hygiene and functionality.
The O-Ring’s Function
The O-Ring, also known as the Mack washer, is crucial. It seals the area between the tank and bowl. A faulty O-Ring can lead to leaks under the tank. Always check it if you find moisture.
The Wax Ring and Floor Flange Connection
The wax ring is key to a leak-free toilet. It seals the toilet to the drainage system. It’s hidden unless you move the toilet. The floor flange firmly secures the toilet to the floor and into the drainage. Together, the ring and flange prevent leaks and movement.
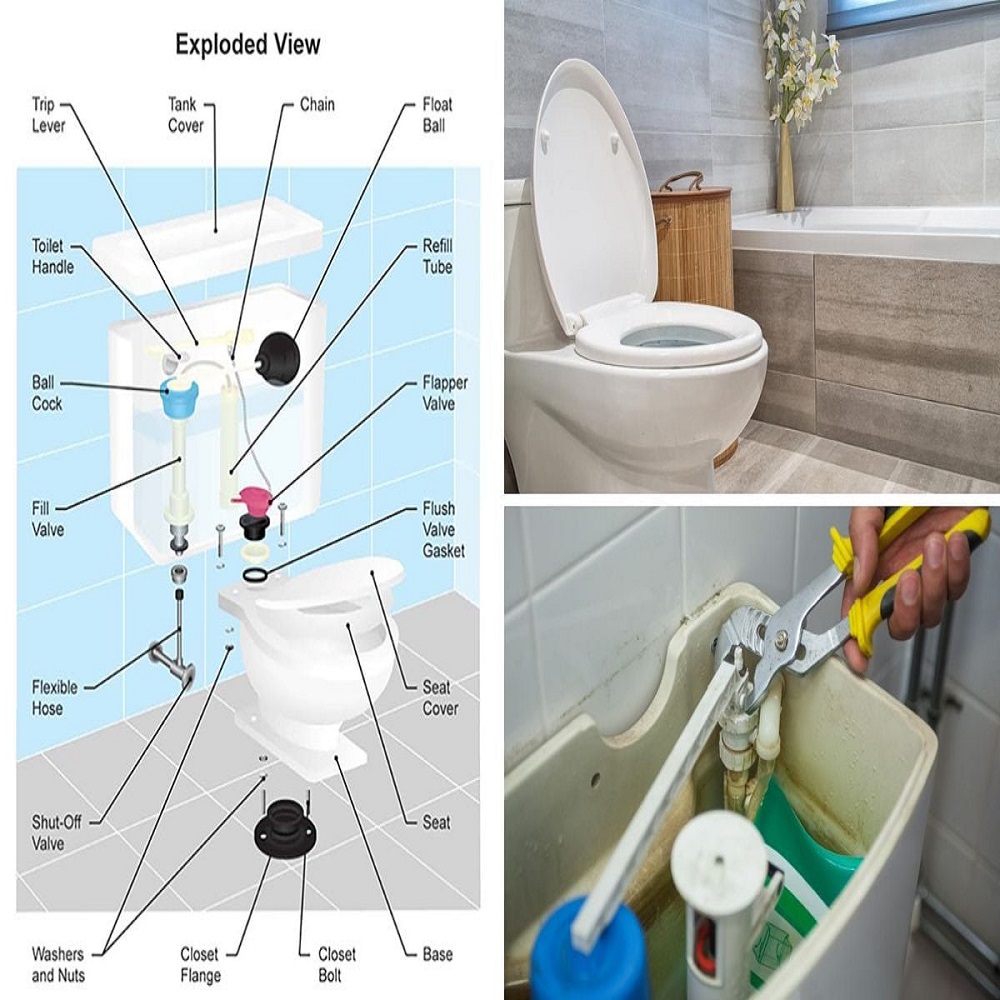

Common Toilet Tank Issues and Solutions
Toilet tanks may seem simple, but issues can arise that affect your bathroom’s hygiene and efficiency. Fixing these common problems can save water and prevent damage to your home. Let’s look at three typical toilet tank issues and how to solve them.
Dealing with a Running Toilet
A running toilet can waste gallons of water and inflate your bills. This is often due to a flapper that doesn’t seal properly or a fill valve that won’t shut off. To fix it, check if the flapper is clean and sits correctly. If it’s warped or damaged, replace it. Adjust or replace the fill valve if it fails to stop water flow after the tank refills.
Toilet Tank Overflows: Prevention and Fixes
Tank overflows can make a mess. They often result from a clogged or incorrectly set float. Clear any blockages in the toilet’s drain or the overflow tube. Adjust the float to ensure the water level is below the overflow pipe. This prevents excess water from spilling out.
Troubleshooting Flapper and Fill Valve Problems
A flapper and fill valve that don’t work right can cause running or weak flushes. If the flapper isn’t sealing, water keeps draining, causing the fill valve to run constantly. Replace a worn flapper or adjust its chain for a proper seal. If the fill valve is faulty, it may not refill the tank properly. Check for debris and clean or replace the valve as needed.
By understanding the anatomy of a toilet and how to address common toilet tank issues, you can ensure a properly functioning and efficient bathroom.
Installation and Maintenance Insights
Understanding how to install and maintain a toilet is key to bathroom functionality. This section covers basic steps and tips. It empowers homeowners to manage some aspects of toilet care.
Steps for Installing a Toilet Tank
Installing a toilet tank involves several clear steps. First, turn off water supply and drain existing tank and bowl. Next, disconnect the water supply from the tank. Remove old tank if replacing. Position new tank on the bowl, ensuring alignment of mounting holes. Insert and tighten bolts connecting tank to bowl, taking care not to over-tighten. Attach water supply to tank’s fill valve. Turn on water supply and check for leaks.
For a new seal, consider a Wax Free option for a hassle-free, durable connection. Test flush to ensure proper operation. Adjust the fill valve and flapper if necessary.
Tips for Ongoing Toilet Maintenance
Regular maintenance prevents common toilet issues from escalating. Check the flapper and fill valve periodically for wear or damage. Clean mineral deposits from tank parts to ensure smooth operation. Inspect the tank-to-bowl gasket to prevent leaks. Adjust the chain length of the flapper for optimal performance.
At least once a year, give toilet a comprehensive check. This includes checking bolts for proper tightness and the condition of the wax ring or wax-free seal.
By following these installation and maintenance insights, you can maintain a well-functioning toilet. This saves water, reduces bills, and avoids unnecessary repairs.
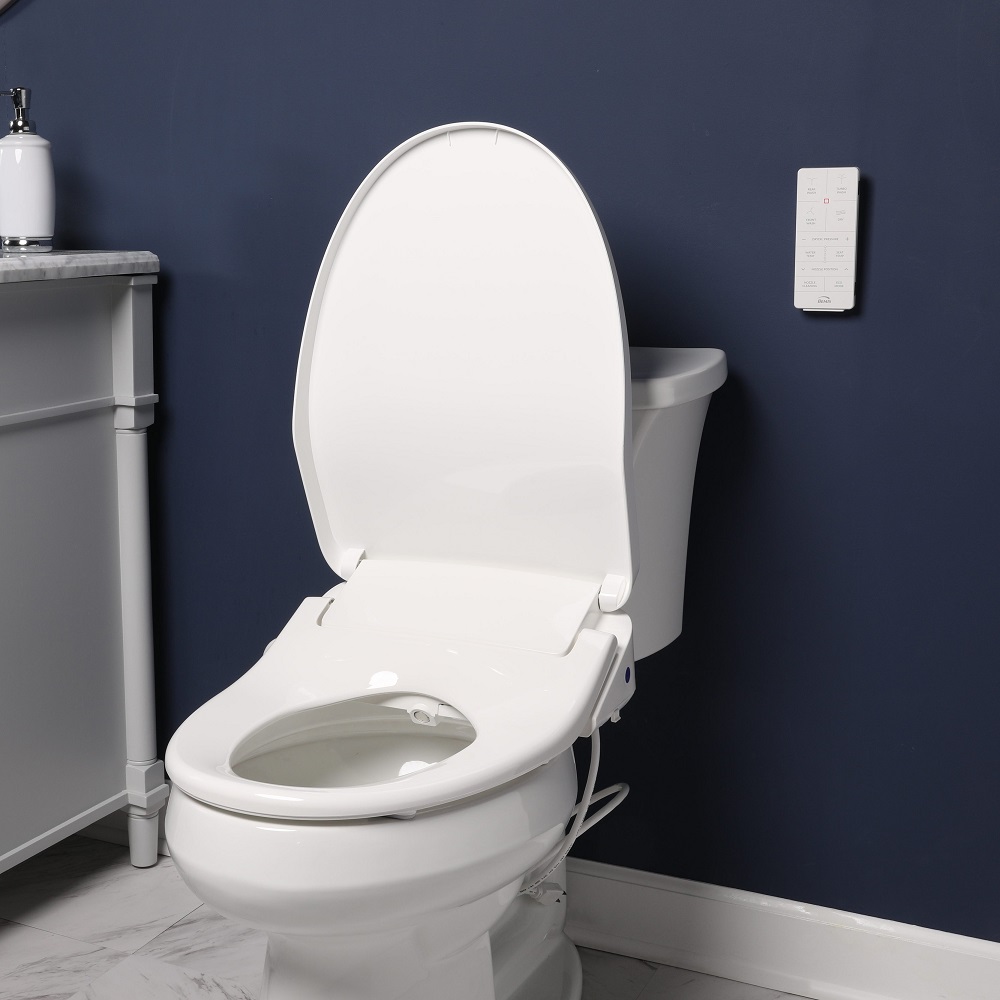

Innovations in Toilet Technology
The anatomy of a toilet has seen significant advancements over the years. Innovations aim to enhance hygiene, efficiency, and user experience.
Bidet Integration and Water Efficiency
Modern toilets often include bidet features, reducing the need for toilet paper. This integration promotes hygiene and saves on paper. Bidet systems use a targeted water spray, which is more effective and gentle. Many models also focus on water efficiency, using less for each rinse. This conservation effort is key in eco-friendly bathroom designs. The combination of bidets and high-efficiency toilets has reshaped our bathroom experiences.
Advances in Flushing Mechanisms and Materials
New flushing systems are designed for power and water conservation. Dual-flush mechanisms let users choose less water for liquid waste. This choice can greatly reduce water use over time. Advances in materials have also been vital. Modern flappers and seals resist decay and leaks longer. In particular, materials resistant to corrosion and hard water extend part life. This results in fewer replacements and better overall function. These materials innovations ensure a flush that is strong and consistent, while still being mindful of water usage.
Conclusion: Enhancing Your Bathroom’s Functionality
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy of a toilet is key to maintaining a smoothly operating bathroom. By learning about each component, from the flush handle and toilet flapper to the fill valve and flush valve, you become adept at pinpointing issues and performing efficient repairs. A solid grasp on the tank-to-bowl gasket and alternatives like the Wax Free Seal is vital for a leak-proof system.
Regular maintenance and an eye on innovations can lead to improvements in bathroom hygiene and efficiency. Installation of modern high-efficiency toilet and integrated bidet systems show the progress in toilet technology. They not only enhance the user experience but are also eco-friendly choices. These advancements, such as dual-flush mechanisms and corrosion-resistant materials, contribute to conserving water while ensuring optimal functionality.
Remember, the perfect flush is a balance of a well-maintained system and the use of current technologies. By keeping the insights shared in this blog in mind, you’ll be set to maximize your bathroom’s functionality and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.