Introduction: The Symbolic Importance of the King’s Chair
The throne, often referred to as the “seat of power,” holds a significant place in the history and culture of monarchies worldwide. From ancient times to modern-day monarchies, the king’s chair has been a symbol of authority, sovereignty, and prestige. In this exploration, we will delve into the rich history and symbolism surrounding the throne, uncovering its majesty and significance.

A Throne Fit for Royalty: Design and Architecture
The design and architecture of the king’s chair reflect not only the wealth and status of the monarch but also the cultural and artistic influences of the time. Thrones are often elaborately craft with luxurious materials such as gold, silver, and precious stones, showcasing the opulence of the monarchy. Intricate carvings, ornate decorations, and symbolic motifs adorn the throne, emphasizing its grandeur and importance.
The Sacred Symbolism of the Throne: Divine Right and Legitimacy
Throughout history, the throne has been imbued with sacred symbolism, representing the divine right of kings to rule and the legitimacy of their reign. In many cultures, monarchs were believing to be appointed by the gods or ordained by divine providence, and the throne served as a tangible manifestation of their authority. The act of ascending the throne symbolized the monarch’s acceptance of their duty to govern and protect their people.

Seated in Power: The Ritual of Coronation
The coronation ceremony, during which the monarch is crowned and seated upon the throne, is a time-honored tradition steeped in symbolism and ritual. The throne becomes the focal point of the ceremony, serving as the stage upon which the monarch is officially invested with power and authority. The act of sitting upon the throne symbolizes the monarch’s assumption of their rightful place as the ruler of the realm, entrusted with the welfare and prosperity of their subjects.
The Throne Room: A Place of Majesty and Majesty
The throne room, where the king’s chair is situated, is often the grandest and most imposing chamber in the royal palace. Designed to inspire awe and reverence, the throne room is adorning with lavish furnishings, magnificent artworks, and intricate tapestries, creating a setting befitting the majesty of the monarchy. It is here that the monarch holds court, receives dignitaries, and presides over ceremonial events, projecting an image of power and authority to all who enter.

The Power Behind the Throne: Advisors and Influences
While the monarch may sit upon the throne as the embodiment of power, they are often surround by advisors, counselors, and influential figures who shape and inform their decisions. The power behind the throne, often referred to as the “royal council” or “courtiers,” plays a crucial role in governance and policy-making, offering counsel and guidance to the monarch. Behind every great ruler is a network of trusted advisors who help steer the course of the kingdom.
Thrones Through Time: From Ancient Empires to Modern Monarchies
The concept of the throne dates back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China, where rulers were elevat above their subjects on ornate ceremonial chairs. Over time, the tradition of thrones evolved and spread to other cultures and regions, becoming synonymous with monarchy and kingship. Today, thrones can be found in monarchies around the world, from the opulent palaces of Europe to the grand halls of Asia and Africa.
The Legacy of the Throne: A Symbol of Continuity and Tradition
The throne carries with it a legacy of continuity and tradition, connecting the present-day monarch to the long line of rulers who came before them. Each successive monarch inherits not only the physical throne itself but also the responsibilities and obligations that accompany it. By sitting upon the throne, the monarch acknowledges their role as a custodian of tradition and a steward of the nation’s heritage, ensuring that the legacy of the monarchy endures for generations to come.
Adapting to the Times: The Evolution of Throne Design
Over the centuries, the design of thrones has evolved to reflect changing tastes, cultural influences, and technological advancements. While ancient thrones were often massive, ornately carved structures adorned with precious metals and jewels, modern thrones tend to be more streamlined and functional, reflecting contemporary design sensibilities. However, despite these changes, the essential symbolism of the throne as a seat of power and authority remains unchanged.
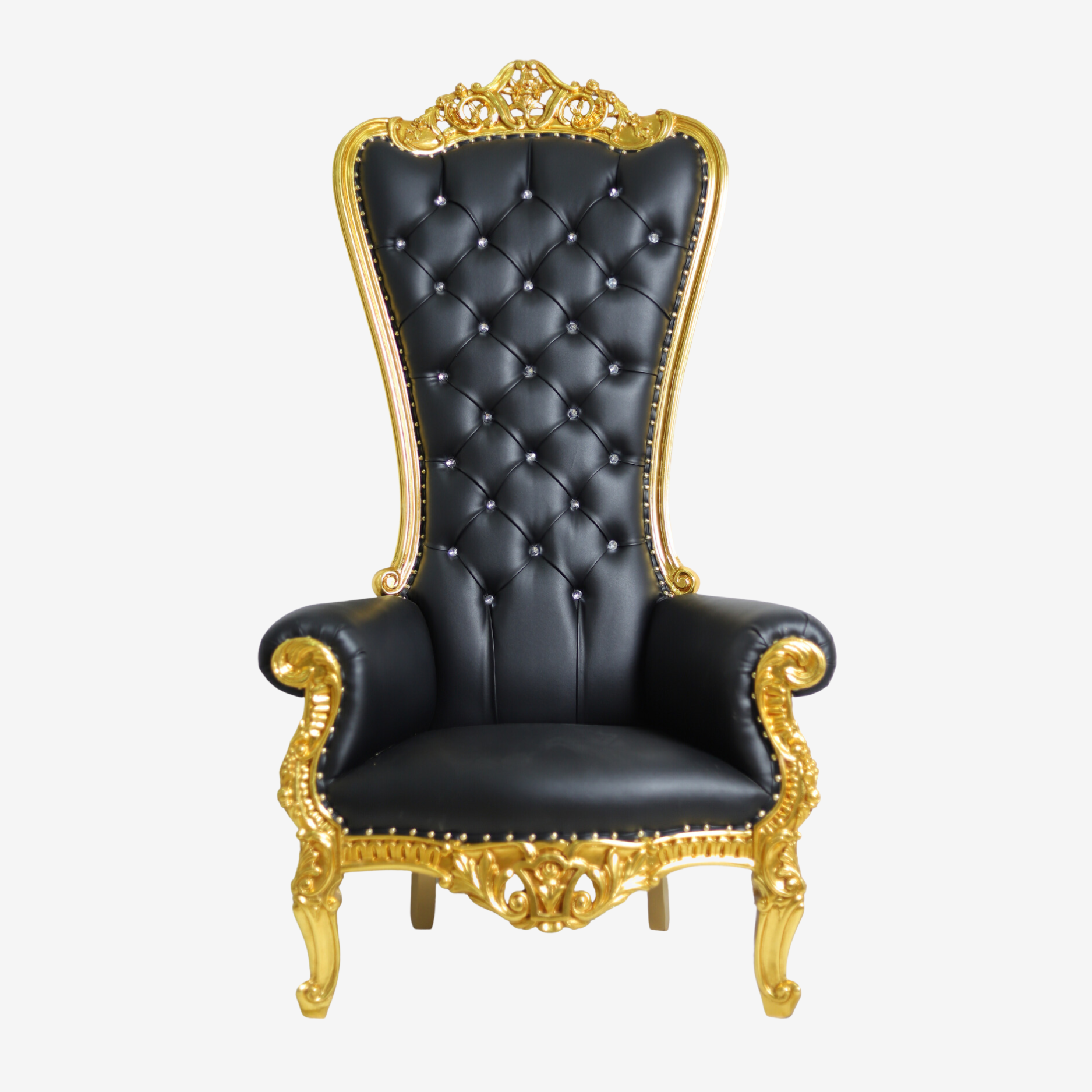

The Global Influence of Thrones: From East to West
Thrones have played a central role in the cultures and traditions of civilizations around the world, from the majestic dragon thrones of imperial China to the regal thrones of European monarchies. Each culture has imbued the throne with its own unique symbolism and significance, reflecting the values and beliefs of its people. Despite these cultural differences, thrones serve as a universal symbol of leadership and sovereignty, transcending geographical and cultural boundaries.
Thrones in the Modern Era: Symbolism in a Democratic Age
In an era of democracy and egalitarianism, the symbolism of the throne may seem antiquated to some. However, even in modern constitutional monarchies where the monarch’s powers are largely ceremonial, the throne retains its symbolic importance as a representation of continuity, tradition, and national identity. While the king or queen may no longer wield absolute authority, the throne serves as a reminder of the historical roots of the monarchy and its enduring role in the governance of the nation.
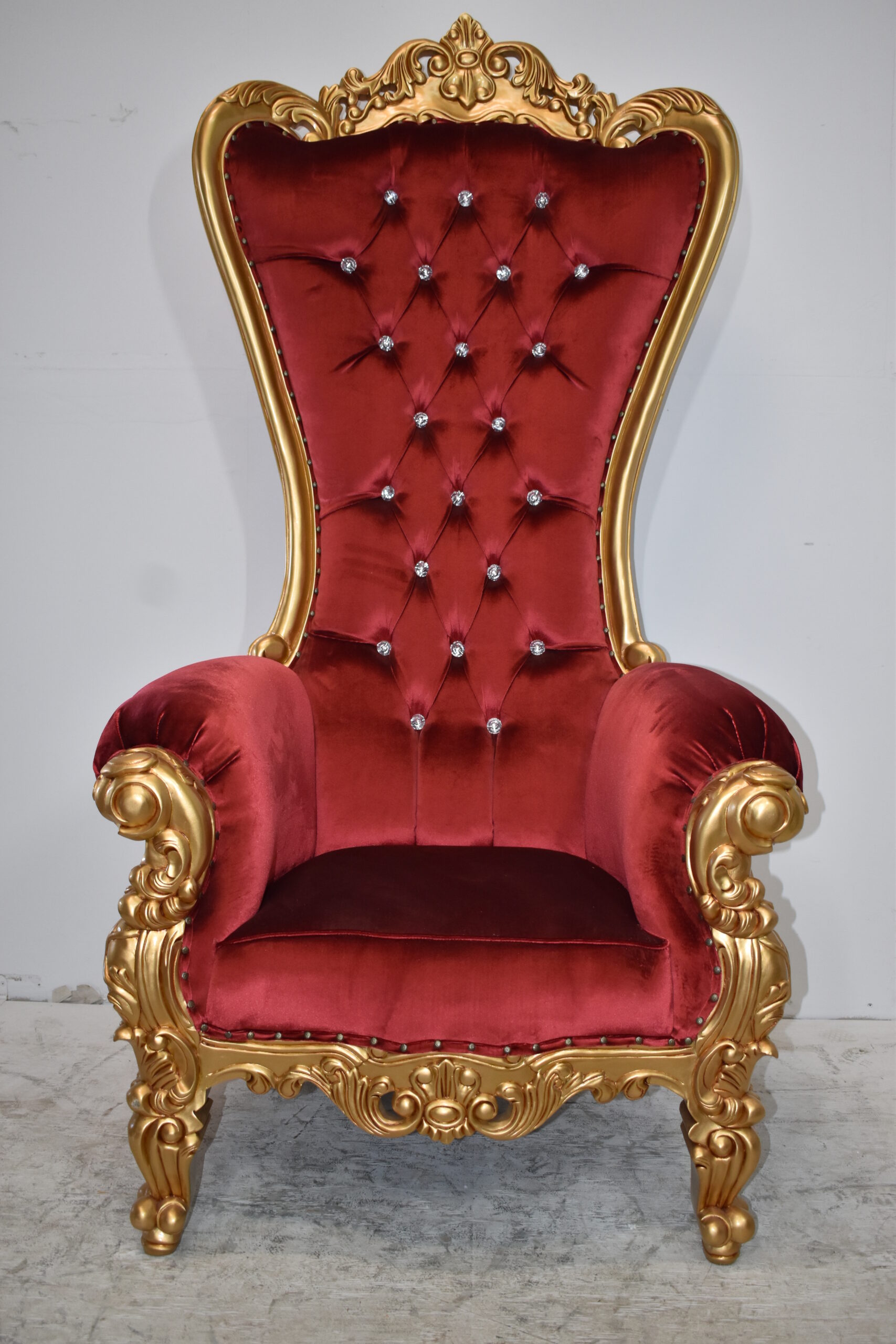

The Throne in Popular Culture: From Fantasy Epics to Political Dramas
Thrones have captured the imagination of storytellers and artists for centuries, appearing in literature, film, and television as symbols of power, intrigue, and ambition. From the Iron Throne of Westeros in George R.R. Martin’s “Game of Thrones” to the throne room of Asgard in Marvel’s “Thor” franchise, thrones continue to fascinate audiences with their symbolic resonance and dramatic potential. Whether depicted as a seat of honor or a coveted prize, the throne remains a potent symbol of authority and aspiration in popular culture.
Conclusion: The Enduring Majesty of the King’s Chair
In conclusion, the throne stands as a timeless symbol of power, authority, and tradition, embodying the majesty and grandeur of monarchy. From its origins in ancient civilizations to its place in modern-day monarchies, the king’s chair continues to inspire awe and reverence, serving as a potent reminder of the enduring legacy of royalty. As long as there are kings and queens to rule, the throne will remain a symbol of sovereignty and splendor, forever enshrined in the annals of history.